- IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm 9.70.x
- C-SPY Debugging
- Memory and registers
- Reference information on memory and registers
- Memory Configuration dialog box for C-SPY hardware debugger drivers
Memory Configuration dialog box for C-SPY hardware debugger drivers
The Memory Configuration dialog box is available from the C-SPY driver menu.
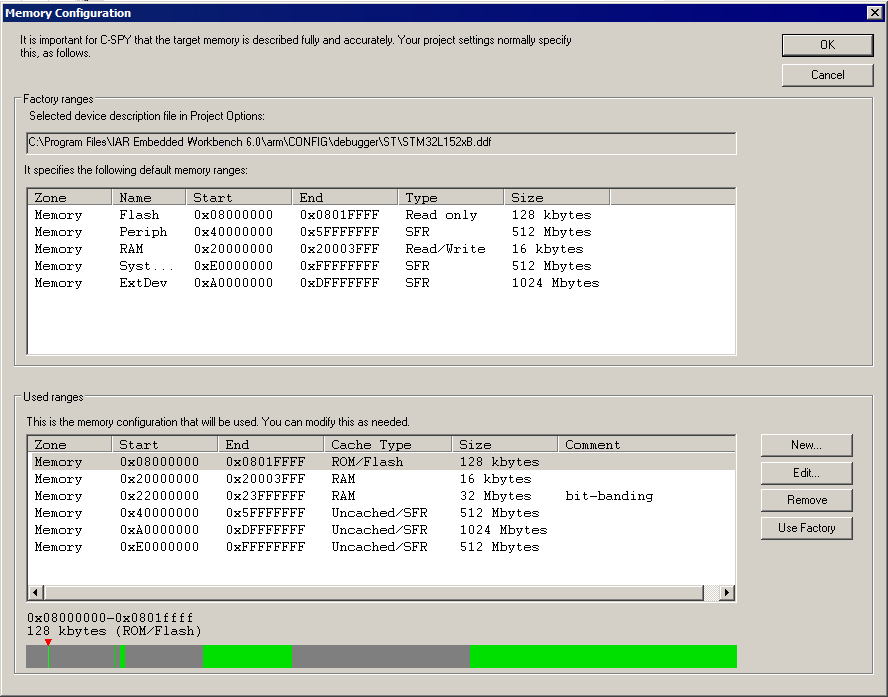
C-SPY uses a default memory configuration based on information retrieved from the device description file that you select, or if memory configuration is missing in the device description file, tries to provide a usable factory default. See Selecting a device description file.
Use this dialog box to verify, and if needed, modify the memory areas so that they match the memory available on your device. Providing C-SPY with information about the memory layout of the target system is helpful both in terms of performance and functionality:
Reading (and writing) memory (if your debug probe is connected through a USB port) can be fast, but is usually the limiting factor when C-SPY needs to update many debugger windows. Caching memory can speed up the performance, but then C-SPY needs information about the target memory.
If C-SPY has been informed that the content of certain memory areas will be changed during a debug session, C-SPY can keep a copy of that memory readable even when the target does not normally allow reading (such as when executing).
C-SPY can prevent accesses to areas without any memory at all, which can be important for certain hardware.
The Memory Configuration dialog box is automatically displayed the first time you start the C-SPY driver for a given project, unless the device description file contains a memory description which is already specified as correct and complete. Subsequent starts will not display the dialog box unless you have made project changes that might cause the memory configuration to change, for example, if you have selected another device description file.
You can only change the memory configuration when C-SPY is not running.
See also Memory configuration for C-SPY hardware debugger drivers.
Requirements
One of these alternatives:
The C-SPY I-jet driver
The C-SPY J-Link/J-Trace driver
The C-SPY ST-LINK driver
The C-SPY CMSIS-DAP driver
The C-SPY GDB Server driver
The C-SPY TI MSP-FET driver
The C-SPY TI Stellaris driver
The C-SPY TI XDS driver
Factory ranges
Identifies which device description file that is currently selected and lists the default memory address ranges retrieved from the file in these columns:
- Zone
The memory zone, see C-SPY memory zones.
- Name
The name of the memory address range.
- Start
The start address for the memory address range, in hexadecimal notation.
- End
The end address for the memory address range, in hexadecimal notation.
- Type
The access type of the memory address range.
- Size
The size of the memory address range.
Used ranges
These columns list the memory address ranges that will be used by C-SPY. The columns are normally identical to the factory ranges, unless you have added, removed, or modified ranges.
- Zone
Selects a memory zone, see C-SPY memory zones.
- Start
The start address for the memory address range, in hexadecimal notation.
- End
The end address for the memory address range, in hexadecimal notation.
- Cache Type
The cache type of the memory address range.
- Size
The size of the memory address range.
- Comment
Memory area information.
Use the buttons to override the default memory address ranges that are retrieved from the device description file.
Graphical bar
A graphical bar that visualizes the entire theoretical memory address range for the device. Defined ranges are highlighted in green.
Buttons
These buttons are available for manual ranges:
- New
Opens the Edit Memory Range dialog box, where you can specify a new memory address range and associate a cache type with it, see Edit Memory Range dialog box for C-SPY hardware debugger drivers.
- Edit
Opens the Edit Memory Range dialog box, where you can edit the selected memory address area. See Edit Memory Range dialog box for C-SPY hardware debugger drivers.
- Remove
Removes the selected memory address range definition.
- Use Factory
Restores the list of used ranges to the factory ranges.