Optimizations
The Optimizations options determine the type and level of optimization for the generation of object code.
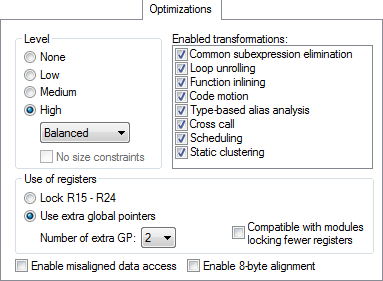
Level
Selects the optimization level. Choose between:
- High
The highest level of optimization. Choose from:
Balanced, the highest level of optimization, balancing between speed and size.
Size, the highest level of optimization, favoring size.
Speed, the highest level of optimization, favoring speed.
By default, a debug project will have a size optimization that is fully debuggable, while a release project will have a high balanced optimization that generates small code without sacrificing speed.
For a list of optimizations performed at each optimization level, see Optimization levels.
Enabled transformations
Selects which transformations that are available at different optimization levels. When a transformation is available, you can enable or disable it by selecting its check box. Choose between:
Common subexpression elimination
Loop unrolling
Function inlining
Code motion
Type-based alias analysis
Cross call
Scheduling
Static clustering
Note
In a debug project the transformations are, by default, disabled. In a release project the transformations are, by default, enabled.
For a brief description of the transformations that can be individually disabled, see Fine-tuning enabled transformations.
Use of registers
These options determine how the compiler treats registers.
- Lock R15 – R24
Locks registers
R15–R24, so that they are left untouched by the compiler. Note that registerR2is always free to use by an operating system, because it is never used by the compiler at all.- Use extra global pointers
Reserves some of the registers
R20–R24for use by the compiler as extra global pointer (GP) registers. Use the Number of extra GP option to specify the number of extra global pointer registers. The reserved registers always start withR20, so if (for example) three registers are used as extra global pointers, it will be registersR20–R22- Compatible with modules locking fewer registers
Links the module being compiled with object files that lock fewer registers than the module. These object files may also use register constants even if they are not used for this module.
This option does not allow definitions or the use of functions that are not compatible when different register locking levels are used. In practice this means an upper limit to the number of parameters to functions.
In order to use this feature at least one register must be locked from use.
Enable misaligned data access
Generates misaligned data accesses for packed structures.
Enable 8-byte alignments
Use this option to enable 8-byte alignment for data types long long and double.