C-RUN Runtime Checking options
What do you want to do?
Learn about:
Learn how to:
Get reference information about the C-RUN Runtime Checking options, see below the line.

The C-RUN Runtime Checking options determine which checks to perform at runtime.
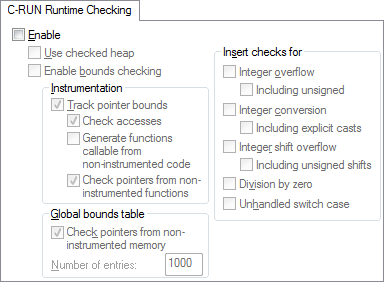
Enable
Enables runtime checking.
Use checked heap
Uses the checked heap, to detect heap usage errors.
Enable bounds checking
Checks for accesses outside the bounds of arrays and other objects. Available checks:
- Track pointer bounds
Makes the compiler add code that tracks pointer bounds. If you want to check pointer bounds, you should enable Check accesses and then decide how instrumented code should interact with non-instrumented code:
Check accesses
Inserts code for checking accesses via pointers.
Generate functions callable from non-instrumented code
When Track pointer bounds is enabled, any functions that return or receive types that contain pointers are modified to also return/receive pointer bounds. Use this option to generate an extra entry for each such function, which can be called from unchecked code.
Check pointers from non-instrumented functions
When Track pointer bounds is enabled, pointers that originate from functions that are not instrumented for bounds checking are by default given globally permissive bounds information. Use this option to identify these pointers—any accesses via such pointers will generate an error. In this way you can manually replace the globally permissive bounds information with valid counterparts, see __as_get_base, __as_get_bound, __as_make_bounds.
If this option is not used and you do not specify valid bounds information, accesses via such pointers do not generate errors and might result in unnoticed incorrect runtime behavior.
Check pointers from non-instrumented memory
When Track pointer bounds is enabled, each time a pointer is loaded from memory, its bounds are looked up in the global bounds table. If no entry is found in the table for this pointer, usually because the pointer was created by non-instrumented code, it is given globally permissive bounds. Use this option to identify such pointers—any accesses via such pointers will generate an error. In this way you can manually replace the globally permissive bounds information with valid counterparts, see __as_get_base, __as_get_bound, __as_make_bounds.
If this option is not used and you do not specify valid bounds information, accesses via such pointers do not generate errors and might result in unnoticed incorrect runtime behavior.
Number of entries
The bounds checking system uses a separate table to track bounds for pointers in memory. Use this option to set the number of such bounds that can be tracked simultaneously. The table will use approximately 50 bytes per pointer.
Insert checks for
Inserts checks for:
- Integer overflow
Checks for signed overflow in integer operations. Use Including unsigned to also check for unsigned overflow in integer operations.
- Integer conversion
Checks for implicit integer conversions resulting in a change of value. Use Including explicit casts to also check for explicit casts.
- Integer shift overflow
Checks for overflow in shift operations. Use Including unsigned shifts to also check for unsigned overflow in shift operations.
- Division by zero
Checks for division by zero.
- Unhandled switch case
Checks for unhandled cases in
switchstatements