Detecting heap memory leaks
Description
Checks for heap blocks without references at a selected point in your application.
Why perform the check
A leaked heap block cannot be used or freed, because it can no longer be referred to. Use this check to detect references to heap blocks and report blocks that are seemingly unreferenced. Note that the leak detection cannot find all possible memory leak cases, a seemingly unreferenced heap block might actually be referenced and a seemingly referenced heap block might actually be leaked.
Note
The leak checker does not currently support multi-threaded environments. The leak checker works by scanning known RAM locations for references to heap blocks. The thread executing the leak check has information about its own stack, but not about the stack of other threads. The missing information can result in both false positives and false negatives.
How to use it
Linker option: ‑‑debug_heap
In the IDE: Project>Options>Runtime Checking>Use checked heap
The checked heap will replace the normal heap for the whole application. The checked heap requires extra heap and stack resources. Make sure that your application has at least 10 Kbytes of heap and 4 Kbytes of stack.
The leak detection check must be called manually. It can either be called at the exit of the application or it can be used for detecting leaked heap blocks between two source points. These functions are defined in iar_dlmalloc.h:
void __iar_leaks_ignore_all(void);Use this function to mark all currently allocated heap blocks to be ignored in subsequent heap leakage checks.
void __iar_leaks_ignore_block(void *block);Use this function to mark a specific allocated heap block to be ignored in subsequent heap leakage checks.
void __iar_check_leaks(void);Use this function to check for leaks.
How it works
The checked heap will replace the normal heap for the whole application. The heap leakage algorithm has three phases:
Scans the heap and makes a list of all allocated heap blocks.
Scans the statically used RAM, the stack, etc for addresses in the heap. If the address matches one of the heap blocks in the list above, it is removed from the list.
Reports the remaining heap blocks in the list as leaked.
See The checked heap provided by the library.
Example
Follow the procedure described in Getting started using C-RUN runtime error checking, but use the Debug heap option.
This is an example of source code that will be identified during runtime:
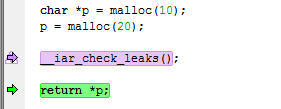
C-RUN will report Memory leak. This is an example of the message information that will be listed:
